Tools
The materials included in this section can be used for self-study and to assist you in delivering presentations to students with disabilities, career development professionals, and employers. Presentations can be delivered at student orientations, staff meetings, conferences, and service club and professional organization meetings. Presentations can be adapted to your audience and schedule. See the Presentations section of this notebook for specific ideas.
Overhead Transparency Templates
Included are black and white templates that can be used as references or copied onto transparencies for use in presentations (see the bottom of this page). A large number of transparencies are included to optimize custom presentation options. Pick and choose the templates that work best for your audience and meeting time.
Video Presentations
Five video presentations are included on the enclosed videotape. They are titled:
- It's Your Career
- Finding Gold: Hiring the Best and the Brightest
- Equal Access: Computer Labs
- Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
- World Wide Access
Handouts
Black and white templates of the following handouts can be copied for distribution to others in your school, at conferences, or during presentations. They are included in the pouch in the back cover of this notebook.
- It's Your Career: Work-Based Learning Opportunities for Students with Disabilities
- Finding Gold: Hiring the Best and the Brightest
- Equal Access: Computer Labs
- Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
- Meet the Speakers in the Videotape -- Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
- World Wide Access: Accessible Web Design
- Meet the Speakers in the Videotape -- World Wide Access: Accessible Web Design
Permission is granted to reproduce printed materials and video presentations for non-commercial, educational purposes as long as credit is given to the source.
Overhead 1
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
No otherwise qualified individual with a disability shall, solely by reason of his/her disability, be excluded from the participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity of a public entity.
Overhead 2
Person with a disability = any person who
- has a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life activities, including walking, seeing, hearing, speaking, breathing, learning, and working
- has a record of such an impairment
- is regarded as having such an impairment
Overhead 3
Examples of Disabilities
Spinal cord injuries
Loss of limbs
Multiple Sclerosis
Muscular Dystrophy
Cerebral Palsy
Hearing impairments
Visual impairments
Speech impairments
Specific learning disabilities
Head injuries
Psychiatric disorders
Diabetes
Cancer
AIDS
Overhead 4
Qualified Individual with a Disability
A "qualified" applicant or employee with a disability is a person with a disability who, with or without reasonable accommodation, can perform the essential functions of the job in question.
Overhead 5
Undue Hardship
An action that requires "significant difficulty or expense" in relation to the size of the employer, the resources available, and the nature of the operation.
Overhead 6
Why Participate in Work-Based Learning?
- Practice skills learned in school.
- Clarify academic and career interests.
- Determine which worksite accommodations work best.
Overhead 7
- Develop contacts for future employment.
- Develop human relations and teamwork skills through interactions with co-workers.
- Gain academic credit.
- Practice writing résumés and cover letters.
- Identify community-based career assistance programs.
Overhead 8
Types of Work Experience
- Internship
- Cooperative Education
- Job Shadowing
- Service Learning
- Independent Study
- Informational Interview
- Career Services
Overhead 9
DO-IT CAREERS
Careers
Academics
Research
Experiential
Education
Relevant
Skills
Overhead 10
Cost of Accommodations |
Percentage |
| 0 | 20% |
| $1 - $500 | 51% |
| $501 - $1,000 | 11% |
| $1,001 - $1,500 | 3% |
| $1,501 - $2,000 | 3% |
| $2,001 - $5,000 | 8% |
| $5,000+ | 4% |
Overhead 11
Recruiting Interns with Disabilities
Include a statement outlining your interest in receiving applications from a diverse group of people, including people with disabilities.
Overhead 12
Advertise available positions with:
- Career Services
- Cooperative Education programs
- Academic Departments
- Disabled Student Services offices
- Division of Vocational Rehabilitation
Overhead 13
- Department of Services for the Blind
- Employment Security
- Governor's Committee on Employment of People with Disabilities
- Community agencies that serve people with disabilities
Overhead 14
Strategies for Working with People Who Have Disabilities
Overhead 15
Low Vision
Blindness
Hearing Impairments
Speech Impairments
Specific Learning Disabilities
Mobility Impairments
Health Impairments
Psychiatric Disabilities
Overhead 16
Low Vision
- Large print handouts, signs, equipment labels
- Seating where the lighting is best
- Work assignments in electronic format
- Computer with enlarged screen images
Overhead 17
Blindness
- Describe visual aids
- Audiotaped, Braille, or electronic text to substitute printed materials
- Raised-line drawings and tactile models of graphic materials
- Adaptive equipment (e.g., tactile timers, calculators)
- Computers with optical character readers, voice output, Braille screen displays, Braille embossers
Overhead 18
Hearing Impairments
- Interpreters, real-time captions, FM systems, note takers
- Electronic mail
- Visual aids, visual warning systems for emergencies
- Face intern when speaking; talk to the intern rather than the interpreter
- Written work assignments
- Repeat questions and statements from other employees during meetings
Overhead 19
Speech Impairments
- Electronic Mail
- Concentrate on what the person is saying
- If you don't understand, ask and repeat back
- Take as much time as necessary to communicate
- Ask questions that require short answers or a nod of the head when appropriate
Overhead 20
Specific Learning Disabilities
- Audiotaped instruction
- Quiet workstation
- Visual, aural, and tactile demonstrations incorporated into directions
- Computers with voice output, spell checkers, grammar checkers, thesaurus, specialized software
Overhead 21
Mobility Impairments
- Office assistants
- Group work assignments, note takers/scribes
- Accessible worksite
- Adjustable tables, equipment located within reach
- Work assignments in electronic format
- Computers with special input devices (e.g., voice, Morse code, alternative keyboards)
Overhead 22
Health Impairments
- Flex time
- Note takers, audiotaped meetings
- Electronic mail
- Work assignments in electronic formats
- Telecommuting
Overhead 23
Psychiatric Disabilities
- Be positive
- Have high expectations
- Be consistent
- Make instructions clear
- Provide positive feedback and suggestions
- Meet with the person
Overhead 24
General Suggestions
- Have policies and procedures in place
- Make sure facility is accessible
- Provide clear signage in large print
- Talk with the worker
- Select materials early
Overhead 25
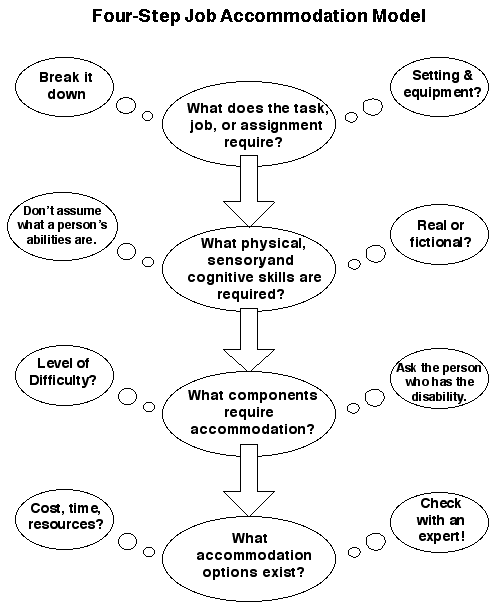
Four-Step Model
- What does the task/ assignment require?
- What physical, sensory, and cognitive skills are needed?
- What components of the task require accommodation?
- What accommodation options exist?
Overhead 26
Overhead 27
Computers
+
Adaptive Technology
+
Electronic Resources
=
Opportunities
Overhead 28
Universal Design
=
designing services and resources for people with a broad range of abilities and disabilities.
Overhead 29
Accessible Labs
- physical environment
- adaptive technology
- electronic resources
Overhead 30
Problem |
Solution |
| access to computers | adaptive technology |
| access to electronic resources | universal design principles |
Overhead 31
Computers assist people with:
- low vision
- blindness
- hearing impairments
- speech impairments
- specific learning disabilities
- mobility impairments
- health impairments
Overhead 32
Low Vision
- large print signs, handouts, labels
- good lighting
- large print key labels
- large monitors
- software to enlarge screen images
- software to adjust screen colors
Overhead 33
Blindness
- Braille and taped materials
- Braille labels
- computers with voice output
- Braille screen displays
- scanners and optical character recognition
- Braille printers
- Internet accessible services/resources
Overhead 34
Hearing/Speech Impairments
- computers with visual output
- electronic mail
- speech synthesizers
Overhead 35
Specific Learning Disabilities
- quiet work areas
- computers with voice output
- spelling/grammar checkers, thesauruses
- word prediction software
- software to enlarge screen images
- large monitors
Overhead 36
Mobility Impairments
- adjustable tables
- keyboard modifications
- keyboard guards and layouts
- alternative keyboards and mice
- Internet services/ resources
Overhead 37
Health Impairments
- electronic mail
- Internet accessible services/resources
Overhead 38
Adaptive Technology
- hardware/software
- easy/difficult to implement
- easy/difficult to use
- inexpensive/expensive
- generic/unique
- stand alone/networked
Overhead 39
Getting Started!
- adjustable tables
- large print key labels
- screen enlargement software
- large monitors
- speech output
- Braille conversion software and printer
- trackballs, wrist rests, keyguards
Overhead 40
Some People:
- cannot see graphics
- cannot hear audio
- have difficulty with unorganized sites
- use older equipment, slow connections
- use adaptive technology
Overhead 41
Universal Design
=
design of products and environments to be usable by all people, without the need for adaptation or specialized design.
Overhead 42
Universal Design Principles
- equitable use
- flexible use
- simple and intuitive use
- information duplicated in several formats
- low physical effort
Overhead 43
Maintain a simple, consistent page layout
Overhead 44
Keep backgrounds simple with enough contrast.
Overhead 45
Make links descriptive so they can be understood out of context.
Overhead 46
Use standard HTML.
Overhead 47
Include a note about accessibility.
Overhead 48
Provide text alternatives.
Overhead 49
Accessible Web Design Guidelines
- Simple, consistent page layout
- Simple backgrounds with enough contrast
- Standard HTML
- Note about accessibility
- Text alternatives for graphical features
- Use special features with care
- Test Web pages with a variety of browsers