Presentation Tools
This section of the notebook includes resources that can be used to prepare for and deliver presentations described in previous sections. These supplies include:
Evaluation Instruments
In this section, you will find two separate evaluation instruments that can be used to gather participant feedback from your presentation.
Presentation Evaluation—Short Form
Please indicate your agreement or disagreement with these statements where 1= Strongly Disagree, 5= Strongly Agree, and N/A= Not Applicable.
- I am better able to find resources on my campus to accommodate students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about legal obligations relating to students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about specific accommodations for students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about technology available to support students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The presenter(s) was (were) well prepared.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - Overall, the information presented was useful.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The handouts will be useful.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A
- The length of the presentation was: about right ____ too short ____ too long ____
- The amount of material was: about right ____ not enough ____ too much ____
- Please tell us about yourself:
____ Male ____ Female
____ Educator ____ Administrator
____ Teaching Assistant ____ Other
Please make specific comments about this presentation on the back of this form.
Presentation Evaluation—Long Form
Part One
Help us know what you learned as a result of this presentation. Please indicate your agreement or disagreement with these statements where 1= Strongly Disagree, 5= Strongly Agree, and N/A = Not Applicable.
- I am better able to find resources on my campus to accommodate students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about legal obligations relating to students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about specific accommodations for students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - I gained knowledge about technology available to support students with disabilities.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A
Please answer the following questions with responses based on today's presentation (as opposed to what you already knew). Describe one thing you learned today about each of the following:
- Legal issues affecting students with disabilities:
- Campus services for students with disabilities:
- Accommodations that can be used for students with disabilities in classes or labs:
Describe additional information you would like to have in order to more fully include students with disabilities in your courses.
Part Two
Please provide input to help us improve our professional development offerings. Please indicate your agreement or disagreement where 1 = Strongly Disagree and 5 = Strongly Agree with the following statements. N/A = Not Applicable.
- The facility for this presentation was appropriate.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The presenter(s) was (were) well prepared.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - Overall, the information presented was useful.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The pace of the presentation was appropriate.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The question and answer time was useful.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A - The handouts will be useful.
1 2 3 4 5 N/A
- Which part of the presentation/material was the most useful to you and why?
- Describe what could make the presentation more useful.
- To whom would you recommend a workshop on this topic (check all that apply)?
____ Educators
____ Teaching Assistants
____ Administrators
____ Other (please specify):________________________________________
- The length of the presentation was: about right ____ too short ____ too long ____
The amount of material was: about right ____ not enough ____ too much ____
Part Three
Please tell us about yourself:
____ Male ____ Female
____ Educator ____ Administrator
____ Teaching Assistant ____ Other
Have you ever provided an accommodation to a student with a disability? Yes__ No___
If yes, please give an example:
Overhead Projection Templates
In this section, you will find overhead projection templates that can be used to create overhead visuals for your presentations. You may also wish to access the PowerPoint containing all slides.
Visual #1
Teaching Students with Disabilities
Science and Math
Visual #2
Science and Math Access Objectives
- Discuss challenges students with disabilities face in gaining and demonstrating knowledge in science and mathematics.
- List examples of accommodations for students with various types of disabilities in science and mathematics courses.
- Describe a process for selecting appropriate accommodations.
Visual #3
Challenges for Students with Disabilities:
- gaining knowledge
- demonstrating knowledge
Visual #4
AccessStem
Visit the AccessStem web page at www.washington.edu/doit/programs/accessstem/overview
Visual #5
Accommodation Strategies
Visual #6
Factors Influencing the Increased Participation of Students with Disabilities in Postsecondary Education:
- survival rate
- technology
- K-12 special education
- awareness
Visual #7
Accommodation Strategies Objectives
- Learn about the rights, responsibilities, contributions, and needs of students with disabilities.
- Summarize institutional and departmental rights and responsibilities for ensuring equal opportunities.
- List strategies for working with students who have disabilities.
- Describe actions that we can take to ensure that students with disabilities have education opportunities equal to those of their nondisabled peers.
- Describe resources.
Visual #8
"A person with a disability" is any person who:
- has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, including walking, seeing, hearing, speaking, breathing, learning, and working
- has a record of such an impairment
- is regarded as having such an impairment
Visual #9
Examples of Disabilities
Low Vision
Blindness
Hearing Impairments
Mobility Impairments
Psychiatric Impairments
Health Impairments
Learning Disabilities
Visual #10
Accommodations for Low Vision
- Seating near front of class
- Good lighting
- Large-print books, handouts, signs, and equipment labels
- TV monitor connected to microscope to enlarge images
- Assignments in electronic format
- Software to enlarge screen images
- Software to adjust screen colors
Visual #11
Accommodations for Blindness
- Printed materials on computer disk and/or on a web page or in email
- Describe visual aids
- Audiotaped, Braille, or electronic notes, handouts, texts
- Raised-line drawings and tactile models of graphic materials
- Braille lab signs, equipment labels
- Auditory lab warning signals
- Adaptive equipment (e.g., talking thermometers, calculators; tactile timers)
- Computer with optical character reader, voice output, Braille screen display printer output
- Increased time on tests
Visual #12
Accommodations for Specific Learning Disabilities
- Note taker and/or audiotaped class sessions
- Captioned videos
- Textbooks on tape
- Visual, aural, and tactile instructional demonstrations
Visual #13
Accommodations for Specific Learning Disabilities, continued
- Course and lecture outlines
- Assignments given in advance
- Computer with speech output, spelling checker, grammar checker
- Extra exam time, quiet testing arrangements
Visual #14
Accommodations for Hearing Impairments
- Interpreter, real-time captioning, FM system, note taker
- Captioned videos
- Visual aids; visual warning system for lab emergencies
- Written assignments, lab instructions, demonstration summaries
- Repeating questions and statements from other students during class
Visual #15
Accommodations for Mobility Impairments
- Note taker/lab assistant; group lab assignments
- Classrooms, labs, field trips in accessible locations
- Adjustable table; equipment located within reach
- Extra exam time, alternative testing arrangements
- Access to online research resources
- Class assignments and materials in electronic format
- Computer with special input device (e.g., speech input, Morse Code, alternative keyboard)
Visual #16
Accommodations for Health Impairments
- Flexible attendance requirements
- Extra exam time, alternate testing arrangements
- Note takers and/or audio recorded class sessions
- Assignments in electronic format
- Internet-accessible services and/or resources
Visual #17
Accommodations for Speech Impairments
- Listen carefully to what the person is saying; if you don't understand, ask student to repeat.
- Relax and take as much time as necessary to communicate.
- Ask questions that require short answers or a nod of the head when appropriate.
- Written communication.
- Email.
Visual #18
Accommodations for Psychiatric Impairments
- Audio recorder, note taker
- Preferential seating near door
- Tests, assignments in alternate formats
- Extended time for taking tests
- Separate, quiet room for testing
- Reviewing academic and behavioral expectations in regular meetings with student
Visual #19
General Suggestions for Making Classes Accessible
- Add a statement to the syllabus inviting students who have disabilities to discuss accommodation needs.
- Select materials early.
- Talk with student about accommodation needs.
- Have policies and procedures in place.
- Make sure facility is accessible.
- Provide materials in electronic formats.
- Provide clear signage in large print.
- Use alternative methods of administering tests and testing comprehension of a subject.
- Use campus disabled student services as a resource.
Visual #20
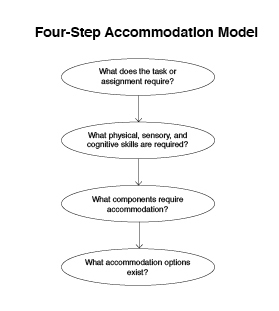
Visual #21
Four-Step Model
- What does the task or assignment require?
- What physical, sensory, and cognitive skills are needed?
- What components of the task require accommodation?
- What accommodation options exist?
Visual #22
Physical, Sensory, and Cognitive Issues and Challenges
Physical Issues
Think of the required physical aspects of the task. What will make the environment accessible, keep the student safe and allow them to be an active participant? What lab equipment must be manipulated?
Physical Challenges
- lift / carry
- stamina / endurance
- push / pull
- kneel / squat
- reach
- repetitive tasks
- fine motor: pinch / grasp
- fine motor: manipulate / maneuver
- gross motor
- sit in chair
- walk / stand
- balance
- bend / twist
- stoop / crouch
- other
Sensory Issues
Think of room temperature, noise, fumes, dust, odors, and allergies. Also consider the ability to speak and/or communicate, and the visual aspects of the task or assignment.
Sensory Issues
- vision
- hearing
- touch
- smell
- taste
- oral communication
- temperature
- fumes
- external stimuli
- lighting
- other
Cognitive Issues
Is the assignment done with a group, partner or individually? What memory and communication skills are needed? What is the level of complexity of the task.
Cognitive Challenges
- short term memory
- long term memory
- task complexity
- reading
- writing
- spelling
- string of numbers (math)
- paying attention
- visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learner.
- self-esteem / advocacy issues
- behavior issues / acting out
- other
Visual #23
Student Abilities Profile
Narrative:
Task/Assignment:
Equipment: (lab equipment, furniture, protective clothing, chemicals, etc.)
Environment: (facility, fumes, odors, dust, temperature, noise, lighting, etc.)
Physical Challenges
Potential Strategies / Accommodations
Resources
Sensory Challenges
Potential Strategies / Accommodations
Resources
Cognitive Challenges
Potential Strategies / Accommodations
Resources
Visual #24
Universal Design of Instruction
Visual #25
Universal Design of Instruction Objectives
- Understand the principles of universal design.
- Apply principles of universal design to instruction to meet a wide range of student learning needs.
- Explain the difference between employing universal design principles to maximize access and providing academic accommodations for students with disabilities.
Visual #26
Diversity
- Ethnic/racial minorities
- English as a second language
- Different learning styles
- People with disabilities
Visual #27
Universal Design =
"The design of products and environments to be usable by all people, without the need for adaptation or specialized design."
Center for Universal Design, North Carolina State University
Visual #28
Principles of Universal Design
- Equitable use
- Flexibility in use
- Simple and intuitive use
- Perceptible information
- Tolerance for error
- Low physical effort
- Size and shape for approach and use
Visual #29
Universal Design of Instruction Examples
- Create an environment that respects and values diversity. Put a statement on your syllabus inviting students to meet with you to discuss disability-related accommodations and other learning needs.
- Ensure that all classrooms labs and fieldwork are in locations accessible to individuals with a wide range of physical abilities and disabilities.
- Use multiple modes to deliver content (including lecture, discussion, hands-on activities, Internet-based interaction, and fieldwork).
- Provide printed or web-based materials, which summarize content that is delivered orally.
- Face the class and speak clearly.
- Use captioned videos.
Visual #30
Universal Design of Instruction Examples, continued
- Provide printed materials in electronic format.
- Use accessible web pages (text descriptions of graphics).
- Provide printed materials early so that students can prepare to access the materials in alternate formats.
- Create printed and web-based materials in simple, consistent formats.
- Provide effective prompting during an activity and feedback after the assignment is completed.
- Provide multiple ways for students to demonstrate knowledge.
- Make sure equipment and activities minimize sustained physical effort.
Visual #31
Making Classroom Activities Accessible to Everyone
- Class lectures
- Classroom discussions
- Internet resources
- Videos
- Course handouts
- Computer and science labs
- Field experiences
Visual #32
Procedures and Outcomes
Instructional Procedures:
- Students will use...
to acquire the course content. - I will use...
to present course content.
Instructional Content:
- Students will describe...
- Students will be able to list...
- Students will demonstrate...
Visual #33
Measuring Instructional Content Versus Procedures
- Evaluation Content:
Students will demonstrate their understanding of... - Testing Procedure:
Students will demonstrate their understanding by...
Visual #34
What barriers to the activity exist for students with the disability your group was assigned?
What accommodation options exist to overcome those barriers?
Visual #35
Fingerprint Accommodations
Visual Impairments
- Position, lighting, and seating needs of student
- Large print, Braille, or electronic handouts and worksheets
- Scanner to create large images
- Clear description of visual aids
- Tactile accommodations
Hearing Impairments
- Sign language interpreter or FM system
- Visual aids
- Clear written directions
- Position and seating (needs to see the instructor/demonstration)
- Instructor communication
Visual #36
Fingerprint Accommodations, continued
Mobility Impairments
- Accessible work space, adjustable tables
- Work with partner
Learning Disabilities/Attention Deficit Disorders
- Multi-modal directions
- Minimize distractions when possible
- Break directions and activity into chunks
Visual #37
M&M'S Ratio Accommodations
Visual Impairments
- Position, lighting, and seating needs of student
- Large print, Braille, or electronic handouts and worksheets
- Talking calculator
- Magnifying glass
- Alternative manipulatives
Hearing Impairments
- Sign language interpreter or FM system
- Visual aids
- Clear written directions
- Position and seating (needs to see the instructor/ demonstration)
- Instructor communication
Visual #38
M&M'S Ratio Accommodations, continued
Mobility Impairments
- Computer-based accommodations
- Larger manipulatives
- Tray to hold manipulatives
- Work with partner
Learning Disabilities/Attention Deficit Disorders
- Multi-modal directions
- Computer-based accommodations
- Reorganize format of documents
- Minimize distractions when possible
- Talking calculator
Visual #39
Surface Area and Volume Accommodations
Visual Impairments
- Position, lighting, and seating needs of student
- Large print, Braille, or electronic handouts and worksheets
- Talking calculator
- Magnifying glass
- Alternative manipulatives
Hearing Impairments
- Sign language interpreter or FM system
- Visual aids
- Clear written directions
- Position and seating (needs to see the instructor/demonstration)
Visual #40
Surface Area and Volume Accommodations, continued
Mobility Impairments
- Computer-based accommodations
- Larger manipulatives
- Tray to hold manipulatives
- Work with partner
Learning Disabilities/Attention Deficit Disorders
- Multi-modal directions
- Computer-based accommodations
- Reorganize format of documents
- Minimize distractions when possible
- Talking calculator
- Break directions and activity into chunks
Visual #41
Information Access
Visual #42
Information Access Objectives
- Describe ways that information is presented in postsecondary institutions.
- Discuss the challenges each mode of information delivery creates for people with different types of disabilities.
- List solutions to the barriers students with disabilities typically face when obtaining information in academic settings.
Visual #43
Academic Context of Information Access
- Classroom work
- Labs
- Homework
- Library
- Web resources
- Distance learning
Visual #44
Information Access Can Be a Challenge for People with
- Visual impairments
- Hearing impairments
- Mobility impairments
- Speech impairments
- Health impairments
- English as a second language
- Alternative learning styles
Visual #45
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
"No otherwise qualified individual with a disability shall, solely by reason of his/her disability, be excluded from the participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity of a public entity."
Visual #46
Access Challenges
- Spoken word
- Printed word
- Video/televised information
- Audio content
- Computer-based information
Visual #47
Access Issues and Solutions
| Problem | Solution | |
|---|---|---|
| access to computers | ⇒ | adaptive technology |
| access to electronic resources | ⇒ | universal design principles |
Visual #48
Making Computing Labs Accessible to Everyone
Visual #49
Making Computer Labs Accessible to Everyone Objectives
- Describe the legal rights of students with disabilities as they relate to computer access.
- Tell how universal design principles can be used to develop computer services that are accessible to all students.
- Discuss steps to be taken to ensure that students with disabilities have access to campus computer labs.
Visual #50
Make Sure Computer Lab Users
- Can get to the facility and maneuver within it
- Access printed materials and electronic resources
- Make use of equipment and software
Visual #51
Adaptive Technology Considerations
- Adjustable tables
- Large-print key labels
- Screen enlargement software
- Large monitors
- Speech output
- Braille conversion
- Trackballs, wrist rests, and keyguards
- Ergonomic keyboards
Visual #52
Access to Computers for Students with Disabilities
Visual #53
Computer Access Objectives
- Describe the legal rights of students with disabilities as they relate to computer access.
- Summarize the issues, needs, and concerns of people with disabilities in accessing electronic resources.
- Describe common types of adaptive technology for students with disabilities.
- Discuss strategies to plan and implement adaptive technology capabilities for campus computer labs/workstations.
Visual #54
Computers assist people with
- Low vision
- Blindness
- Hearing impairments
- Speech impairments
- Learning disabilities
- Mobility impairments
- Health impairments
Visual #55
Low Vision
- large-print signs, handouts, labels
- good lighting
- large-print key labels
- large monitors
- software to enlarge screen images
- software to adjust screen colors
Visual #56
Blindness
- Braille and audio-recorded materials
- Braille labels
- computers with voice output
- Braille screen displays
- scanners and optical character recognition
- Braille printers
- Internet-accessible services/resources
Visual #57
Hearing/Speech Impairments
- computers with visual output
- speech synthesizers
Visual #58
Learning Disabilities
- accessible technology provides multi-sensory experiences
- speech input/output
- spell checkers, thesauruses, and grammar checkers
- word prediction software
- large-print displays and alternative colors on the screen
Visual #59
Mobility Impairments
- adjustable tables
- keyboard modifications
- keyboard guards and layouts
- alternative keyboards and mice
- Internet services/resources
Visual #60
Health Impairments
- Internet-accessible services/resources
Visual #61
Adaptive Technology
- hardware/software
- easy/difficult to implement
- easy/difficult to use
- inexpensive/expensive
- generic/unique
- stand-alone/networked
Visual #62
Getting Started!
- adjustable tables
- large-print key labels
- screen enlargement software
- large monitors
- speech output
- Braille conversion software and printer
- trackballs, wrist rests, keyguards
Visual #63
Universal Design of Web Pages
Visual #64
Universal Design of Web Pages Objectives
- List potential barriers to accessing information on web pages for students with disabilities.
- Describe the institution's legal responsibility to ensure access to information presented on web pages.
- Describe universal design guidelines for developing accessible web pages.
Visual #65
Some Internet Visitors:
- cannot see graphics
- cannot hear audio
- have difficulty with unorganized sites
- use older equipment with slow connections
Visual #66
ADA and the Internet
"Covered entities that use the Internet for communications regarding their programs, goods, or services must be prepared to offer those communications through accessible means as well."
—United States Department of Justice (ADA Accessibility,1997)
Visual #67
Provide Multiple Means of
- representation
- expression
- engagement
Visual #68
"The power of the web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspect."
—Tim Berners-Lee, World Wide Web Consortium
Visual #69
Web Page Development Accessibility Options:
- Avoid inaccessible data types and features.
- Create alternative methods/formats.
Visual #70
Example of a Web Accessibility Statement
"The DO-IT pages form a living document and are regularly updated. We strive to make them universally accessible. We minimize the use of graphics and photos, and provide descriptions of them when they are included. Video clips are open-captioned, providing access to users who can't hear the audio. Suggestions for increasing the accessibility of these pages are welcome."
Visual #71
Test Your Web Pages:
- with different operating systems and monitors
- with different browsers and with audio and graphics-loading features turned off
- with a text browser
- with an accessibility testing program (e.g., Bobby)
- by accessing with the keyboard alone
Visual #72
Policy Guidelines
- Disseminate information
- Train
- Support
- Enforce or reward
- Evaluate and revise
Visual #73
Universal Design of Distance Learning
Visual #74
Universal Design of Distance Learning Objectives
- List potential barriers to distance learning courses for students with disabilities.
- Describe educators, staff, and institutional roles and responsibilities for ensuring equal access to distance learning courses.
- Discuss universal design guidelines for developing accessible distance learning courses.
Visual #75
Accessibility Indicators for Students
- The distance learning home page is accessible to individuals with disabilities (e.g., it adheres to Section 508, World Wide Web Consortium, or institutional accessible-design guidelines/standards).
- A statement about the distance learning program's commitment to accessible design for all potential students, including those with disabilities, is included prominently in appropriate publications and websites along with contact information for reporting inaccessible design features.
Visual #76
Accessibility Indicators for Students, continued
- A statement about how distance learning students with disabilities can request accommodations is included in appropriate publications and web pages.
- A statement about how people can obtain alternate formats of printed materials is included in publications.
- The online and other course materials of distance learning courses are accessible to individuals with disabilities.
Visual #77
Accessibility Indicators for Distance Learning Designers
- Publications and web pages for distance learning course designers include:
- a statement of the program's commitment to accessibility,
- guidelines/standards regarding accessibility, and
- resources.
- Accessibility issues are covered in regular course designer training.
Visual #78
Accessibility Indicators for Distance Learning Instructors
- Publications and web pages for distance learning instructors include:
- a statement of the distance learning program's commitment to accessibility,
- guidelines/standards regarding accessibility, and
- resources.
- Accessibility issues are covered in training sessions for instructors.
Visual #79
Accessibility Indicators for Program Evaluators
- A system is in place to monitor the accessibility of courses and, based on this evaluation, the program takes actions to improve the accessibility of specific courses as well as update information and training given to potential students, current students, course designers, and instructors.
Visual #80
Distance Learning Tools
- Real-time "chat"
- Web pages
- Teleconferencing
- Printed materials
- Videos
Videos
DO-IT Careers 1
- Learn and Earn: Tips for Teens. Students with disabilities show how they benefit from work-based learning. (13 minutes, © 2001)
- Learn and Earn: Supporting Teens. Learn how parents, teachers, and mentors can encourage teens to participate in work-based learning. (13 minutes, © 2001)
- It's Your Career. College students with disabilities tell about the value of work-based learning. (13 minutes, © 1997)
- Access to the Future: Preparing Students with Disabilities for Careers. Learn how to make career services accessible to students with disabilities. (14 minutes, © 2000)
DO-IT College 1
- Working Together: Faculty and Students with Disabilities. Successful students with disabilities tell about techniques and accommodations that contributed to their success, emphasizing the importance of the faculty-student relationship. (9 minutes, © 1994)
- Building the Team: Faculty, Staff, and Students Working Together. Learn how to create an inclusive postsecondary learning environment. (16 minutes, © 2001)
- Equal Access: Universal Design of Instruction. Learn to make instruction in a classroom or tutoring center accessible to all students. (13 minutes, © 2006)
- Equal Access: Student Services. Learn how to apply universal design principles to make postsecondary student services accessible to all students. (15 minutes, © 2004)
DO-IT Programs 1
- DO-IT Pals: An Internet Community. Peers and mentors with disabilities support each other in an online community. (9 minutes, © 2005)
- DO-IT Scholars. High school students with disabilities prepare for college and careers. (11 minutes, © 1994)
- Snapshots: The DO-IT Scholars. DO-IT participants tell about their experiences. (28 minutes, © 1998)
- Finding Gold: Hiring the Best and the Brightest. Employers in work-based learning programs show how to fully include participants with disabilities. (7 minutes, © 1998)
DO-IT Programs 2
- How DO-IT Does It. Successful practices employed by DO-IT programs to increase the success of young people with disabilities in college and careers. (34 minutes, © 2004)
- Opening Doors: Mentoring on the Internet. Mentors help students with disabilities achieve success in college studies and careers. (14 minutes, © 1998)
DO-IT STEM 1
- Working Together: Science Teachers and Students with Disabilities. Successful science students with disabilities suggest ways to make science activities accessible. (13 minutes, © 1998)
- Equal Access: Science and Students with Sensory Impairments. Students and employees with sensory impairments share strategies for success. (14 minutes, © 2005)
- The Winning Equation: Access + Attitude = Success in Math and Science. Science and math teachers share strategies for making these subjects accessible to students with disabilities. (15 minutes, © 1998)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics at the University of Washington. Students and faculty highlight STEM programs offered to a diverse student body at the UW. (10 minutes, © 2000)
DO-IT Technology 1
- Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology. Individuals with disabilities demonstrate adaptive technology for people with mobility impairments, blindness, low vision, hearing and/or speech impairments, and learning disabilities. (14 minutes, © 2000, 1995)
- Working Together: Computers and People with Mobility Impairments. People with mobility impairments demonstrate computer access technology. (14 minutes, © 2001)
- Working Together: Computers and People with Sensory Impairments. People with visual and hearing impairments demonstrate computer technology for school and work. (11 minutes, © 2001)
- Working Together: Computers and People with Learning Disabilities. Students and workers with learning disabilities demonstrate computer-based tools and strategies. (12 minutes, © 2000)
- Computer Access: In Our Own Words. Students with disabilities demonstrate adaptive technology and computer applications. (10 minutes, © 2002)
DO-IT Technology 2
- Equal Access: Computer Labs. Learn how computer labs can be designed as to be accessible to students with disabilities. (11 minutes, © 2006)
- World Wide Access: Accessible Web Design. People with disabilities describe roadblocks they encounter and examples of accessible web design. (11 minutes, © 2002, 1996)
- Real Connections: Making Distance Learning Accessible to Everyone. Learn issues to consider when designing courses to fully include students with disabilities. (12 minutes, © 2002)
- Access to Technology in the Workplace: In Our Own Words. Employees show how to make technology accessible. (13 minutes, © 2004)
- Camp: Beyond Summer. Learn how to add Internet experiences to summer camp programs for children and youth with disabilities. (10 minutes, © 1998)
DO-IT Transition 1
- College: You Can DO-IT! College students with disabilities and staff share advice for success in college. (14 minutes, © 1996)
- Moving On: The Two-Four Step. How to successfully transition from two- to four-year postsecondary institutions. (11 minutes, © 1998)
- Taking Charge 1: Three Stories of Success and Self-Determination. Successful young people with disabilities share strategies for living self-determined adult lives. (17 minutes, © 2001)
DO-IT Self-Determination 1
- Taking Charge 1: Three Stories of Success and Self-Determination. Successful young people with disabilities share strategies for living self-determined lives. (17 minutes, © 2001)
- Taking Charge 2: Two Stories of Success and Self-Determination. Teens with disabilities share how they are learning to live self-determined lives. (15 minutes, © 2006)
- Taking Charge 3: Five Stories of Success and Self-Determination. This video combines the five stories presented in Taking Charge 1 & 2 videos. (27 minutes, © 2006)
Part of Me, Not All of Me
- Part of Me, Not All of Me. Teens with disabilities share their interests, activities, and other aspects of their lives showing that their disabilities do not define who they are. (6 minutes, © 2007)
Handouts
Access to the Future: Preparing College Students for Disabilities and Careers
Beyond Summer: Conducting Internet Activities at Camp
Equal Access: Science and Students with Sensory Impairments
Equal Access: Universal Design of Computer Labs
Equal Access: Universal Design of Distance Learning
Equal Access: Universal Design of Instruction
Equal Access: Universal Design of Student Services
Finding Gold: Hiring the Best and the Brightest
It's Your Career: Work-Based Learning Opportunities for College Students with Disabilities
Learn and Earn: Supporting Teens
Learn and Earn: Tips for Teens
Opening Doors: Mentoring on the Internet
Real Connections: Making Distance Learning Accessible to Everyone
Taking Charge: Stories of Success and Self-Determination
Universal Design of Instruction (UDI): Definition, Principles, Guidelines, and Examples
Universal Design of Web Pages in Class Projects
Web Accessibility: Guidelines for Administrators
The Winning Equation: Access + Attitude = Success in Math and Science
Working Together: Computers and People with Learning Disabilities
Working Together: Computers and People with Mobility Impairments
Working Together: Computers and People with Sensory Impairments
Working Together: Faculty and Students with Disabilities
Working Together: K-12 Teachers and Students with Disabilities
Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
Working Together: Science Teachers and Students with Disabilities